Passive (i.e. battery-free) electric guitar circuits are relatively simple and the possibilities for customization
are endless. A basic understanding of pickups, potentiometers, capacitors and switches is all you need to get
creative and take more control of your instrument’s voice on an electronic level.
Where does the electric guitar signal come from?
Pickups are transducers that convert the mechanical energy of a vibrating guitar string into electrical energy by
way of electromagnetic induction. It is a fundamental concept studied in physics and electronics that a changing
magnetic field will generate a current through a coil of wire. The electric guitar pickup uses permanent magnets
and pole pieces to form a steady magnetic field in the vicinity of each individual guitar string. An opposite
magnetic polarity is induced in the metallic (steel core) guitar string when mounted above its respective pole piece
and when the string moves, the otherwise steady magnetic field changes accordingly. Wire is wrapped around the
poles thousands of times to form a coil within the magnetic field to pick up an induced current and voltage.
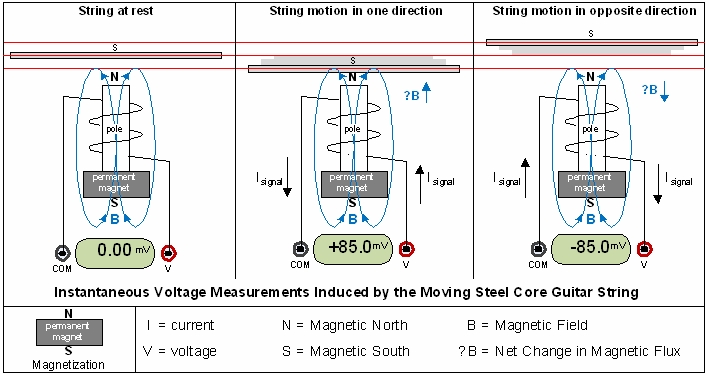
The output signal from the pickups is AC (alternating current) because the direction of the current alternates,
producing a positive voltage when the string moves in one direction and a negative voltage when the string moves in
the opposite direction.
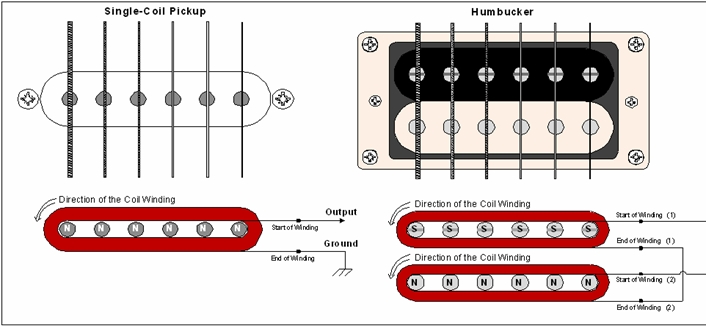
The previous drawing illustrates the electrical and magnetic function of a single-coil pickup. Some pickups might
use six permanent magnets in place of the six pole pieces to create the magnetic field, but the idea is the same:
create a steady magnetic field around a coil in proximity to the guitar string. The name "single-coil" pickup
becomes more significant when compared to the humbucker or "dual-coil" pickup.
Pickups: Single-Coil vs. Humbucker
The first successful guitar pickup was developed in the early 1930’s by Rickenbacker® to help amplify Hawaiian
lap steel guitars which were popular at the time. The first pickups were single-coils and while they do a good
job of picking up the guitar signal they are also susceptible to picking up interference from nearby electrical
devices. The Gibson® humbucker (US Patent 2896491) was developed in the 1950’s to eliminate the “hum noises”
resulting from electromagnetic interference. The humbucker uses two coils and a pair of pole pieces
(having opposite magnetic polarities of each other) for each string. The coils are wound and connected to each
other in such a way that the current produced by the moving guitar string in the two coils adds up (in-phase),
while the current produced by electromagnetic interference in the two coils cancels (out-of-phase). Not only
does the humbucker drastically reduce noise from interference, but it also has a different characteristic sound.
The single-coil pickup is commonly considered to have a thin, clear and bright (more treble) sound, while the
humbucker is known to have a full, but dark (less treble) sound with more overall signal output.
Connecting Multiple Pickups
When connecting more than one pickup, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s color codes and wiring diagrams
so that the phase relationship is correct. The phase relationship of a pickup is determined by the winding
direction of the coil and the polarity of the magnets. The two coils of the traditional humbucker are connected
in series with the phase relationship shown in Fig. 1. Most modern Stratocaster® style guitars with three
single-coil pickups are supplied with a reverse wound/reverse polarity middle pickup for a parallel hum canceling
effect when the guitar is switched to a two pickup position (e.g. neck & middle pickup together) as shown in
Fig. 2.
Pickup Specs
Most replacement electric guitar pickups have limited electrical specifications given on the packaging or on-line
which can give you a basic idea of the relative output level and how bright or dark a similar pickup
will sound.
- DC Resistance: This can be measured directly with an ohm meter and gives you an idea of how many turns of
wire the coil has. If the same gauge of wire was used for two pickups, then the pickup with fewer turns to the
coil will have a lower resistance which, in general, makes for a lower output level and a brighter sound.
- Inductance: Inductance is the ability of an inductor (or coil) to store energy in a magnetic field.
A higher inductance makes for a higher output level and a darker sound.
- Peak Frequency: This is the frequency beyond which the output level begins to fall dramatically.
A higher peak frequency would make for a brighter pickup.
Variety is the spice of tone.
Guitar pickups are a vital component of your tone and replacing them is something that most guitarists can learn
to do themselves. Using high quality pickups can go a long way to bringing new life and excitement to your
playing experience. There are hundreds of pickup manufacturers and thousands of pickups to choose from.
Whether you’re looking for a hotter pickup, trying to capture a beloved vintage tone or seeking single-coil
sound in a noiseless package, brands like DiMarzio®, Seymour Duncan®, Lace®, Porter®, Fender®, Gibson® and many
others offer a solution.
Basic electric guitar circuits - part 2 (Potentiometers and Tone Capacitors)
Basic electric guitar circuits - part 3 (Switches and Output Jacks)
Kurt Prange (BSEE) is the Sales Engineer for
Amplified Parts in Tempe, AZ. Kurt began
playing guitar at the age of nine in Kalamazoo, MI. He is a guitar DIY’er and tube amp designer who
enjoys helping other musicians along in the endless pursuit of tone.

